Earlier this month casino operator Crown Resorts announced a buy-back of up to 4.2% of its outstanding shares, which builds on the $500 million of stock the company had already bought back over the past 12 months. Despite this prima facie positive announcement Crown has fallen 9% in August as the market looked past the buy-back and focused on concerns about returns from the $1.5 billion Sydney Casino.
In last week’s piece give me my money back, we looked at buy-backs that have a positive influence on a company’s share price. However, as you can see with the Crown example, buy-backs are not always positive. This week in the second part of our deeper dive into buy-backs, we are going to look at bad buy-backs and the cheapest ones of all to execute: the fake buy-backs that create the illusion of share price support.

Bad Buy-backs
Theoretically, a company should raise capital when the market is over-valuing their company, and buy back their shares when the market is undervaluing their company. One of the greatest examples in history of a company using their over-valued stock to make an acquisition was dial-up internet company AOL’s US$164 billion purchase of Time Warner in 2000. By issuing shares, AOL shareholders ended up owning the majority of the new media entity, despite Time Warner having significantly more assets and revenue, and ultimately a viable business. In 2009, Time Warner spun off AOL for $3 billion, 2% of the entity’s value in 2000.
Buybacks should only be pursued when management is very confident the shares are undervalued, as companies are no different than regular investors. If a company is buying up shares for $20 each when they are only worth $10, the company is clearly making a poor investment decision
Lack of options
Sometimes buy-backs may be taken as a signal of a lack of attractive growth opportunities in which the company can invest. Particularly in the case of cyclical companies such as miners and airlines, bad buy-backs are conducted after a period of buoyant activity. They are typically done at the top of the cycle, when the costs to develop news assets or buy competitors are at their highest. Whilst this is clearly preferable to a large acquisition such as Rio Tinto’s purchase of Alcan, this approach to capital management often this leaves the company operating in a cyclical industry vulnerable during the inevitable downturns. We view that in some situations it may be best for companies to hoard cash at the top of the stock-market cycle and use it in the next trough to buy back shares at a discount or buy the assets of distressed competitors.
This week BHP resisted the urge to follow Rio Tinto’s lead in announcing a buy-back funded by the sharply increased profits from high commodity prices, ultimately funded by a 2016 Chinese stimulus plan. By paying off debt, BHP may have more options when commodity prices come off.
Offset dilution from executive stock options
Another situation where buybacks are not positive is where they are done to offset the dilution from executive stock options being exercised. This is more common in the US where stock options often form a bigger component of remuneration, but here there is no earnings per share accretion as the number of shares on issue don’t change. This is a poor outcome for shareholders, as the new shares issued to executives via stock options are exercised at a discount to the prevailing share price and those bought via buy-backs are bought on market at the current price! In 2015, IT networking company Cisco Systems bought back 155 million shares, but after the effects of employee stock compensation it only reduced the total shares outstanding by 38 million. Here the buy-back is not capital management, but executive remuneration.
Short term sugar hit to the share price
Many listed companies award senior management bonuses based on the share price of the company they manage. This provides management with an incentive to recommend actions that may deliver a short-term boost to the company’s share price, such as a large buy-back delivering earnings accretion over a long-term investment opportunity. Companies deliver long term growth in their business by investing in future growth.
Buy high sell low
When a company either issues new shares to the market via a placement or buys back their own shares, they are effectively acting as a fund manager in valuing their own shares, making a judgement as to whether their shares are cheap or expensive. However, company management teams have access to a far greater array of information on their company’s finances and future prospects than an external investor could ever hope to have.
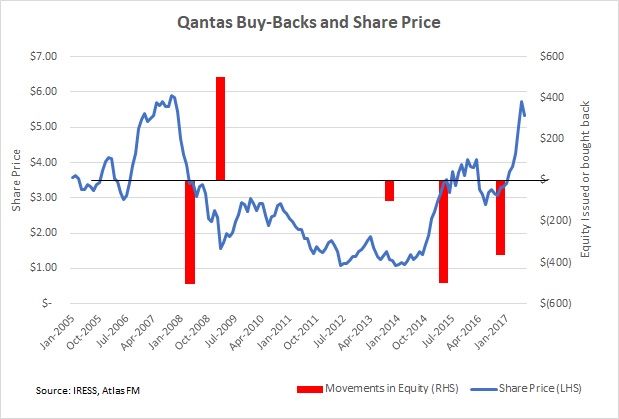
Qantas has a long history of capital management, buying back $506M worth of stock in 2008 (average price $5.56), $100M in 2013 (average price $1.45), $500M in 2016 (average price $3.50), and $366M in 2017 (average price $3.32). However in between was a large equity issue of $525 million shares QAN issued at $1.85 in 2009, and in 2014 Qantas’ debt was rated as junk, as the CEO lobbied the federal government for a bail-out of the then embattled national carrier.
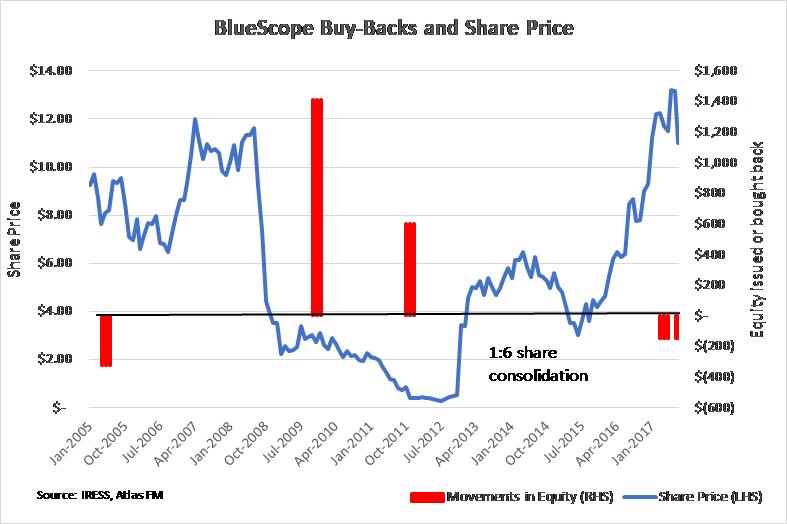
Similarly, steelmaker BlueScope is currently buying back stock over 80% above the level at which it issued over $2 billion in equity not so long ago. Certainly, this has pushed up the share price along with some solid profit growth. However, one may think that retaining capital rather than buying-back shares could prove to be a more prudent cause of action for the steel company. Two years ago, BlueScope were seeking assistance from the government with their struggling Port Kembla steelworks in New South Wales and the company announced a $1 billion loss in 2012!
Fake Buy Backs
In some situations, the company announces the buy-back and enjoys a short-term bounce in the share price without actually buying much in the way of stock. In the listed property trust space, the buy-back often acts to support the price at NTA. For example, in 2014 SCA Property Group announced its intention to undertake an on-market buy-back of up to 5% of its units, as the price jumped above NTA ultimately no units were bought and the buy-back faded into the ether.
Unlike property trusts that have a reference point of net tangible assets per share, it is harder for industrial companies to justify announcing a buy-back and then sitting on their hands. Building materials company CSR last bought back a share in its $150M buy-back in late September. Platinum Asset Management are yet to open their wallet for their $300M share buy-back, also announced last September. Insurer QBE announced a $1 billion buy-back in February, but bought their first share back on 21 August.
Our take
Whilst we are generally in favour of companies returning excess capital to investors rather than retaining it, we concede that not all buy-backs are in the best long-term interest of shareholders. Companies that are returning all their earnings to shareholders may not be investing in research and development or new growth projects. These strategies are necessary to generate returns over the longer term that are ahead of inflation.

