Investing in equities is a long game, with share prices in the short-term influenced by market emotions, forced selling, and Trump tweets – factors that often have very little to do with a company’s profits and growth prospects. However, over the longer term, companies that generally reward their patient shareholders with a higher share price are those that grow earnings and navigate their way through the issues that markets, regulators and their customers throw at them.
Next week the 2010s will come to a close, a decade that has generally been very kind to investors in Australian equities with the ASX 200 up by 130%. In this week’s piece, we are going to look at how Australian equities have fared over the past ten years, along with the key themes that have influenced the share market during this period.
Setting the Scene
December 2009 was a pretty bleak period for investors. While the ASX 200 had recovered from its low in February 2009, investor confidence remained very fragile. The Babcock and Brown group of companies had just gone into administration and Centro was looking very shaky. Over the course of 2009, ASX listed companies had raised a record $70 billion in hurried rights issues and placements to shore up company balance sheets, placating the banking wolves howling at their doors. The 2009 financial reporting year was one to forget with companies delivering weaker profits and writing down the value of assets acquired in the heady days before the GFC.

Key Factors
While management teams can grow earnings via expanding into new markets, taking market share from competitors, and making acquisitions (or selling unprofitable businesses), external factors over which a company’s management has no control such as exchange rates, commodity prices and interest rates often have the biggest impact on a company’s profits and thus share prices. Over the past decade, the Australian Dollar vs the US Dollar has declined from US$0.90 to US$0.68 after peaking at $1.10 in 2011. The 25% decline in the Australian dollar in the 2010s has steadily boosted the earnings of companies such as CSL (+885%), Amcor (+266%) and Sonic Healthcare (+154%), all of which derive most of their profits from operations outside Australia.
Similarly, the steady decline in interest rates over the past decade has reduced interest costs for all Australian companies, increasing profits after tax. In January 2010 the benchmark Australian Government ten-year bond rate was 5.7%, but it finished the decade at a low of 1.29%. For households over this period borrowers have seen the standard variable rate decline from 6.9% to 3.3%. On a $700,000 loan, this would cause monthly payments to decline from $4,900 to $3,430 per month. While falling interest rates saw Australian credit growth increase from 0% to 12% in 2016, over the past four years credit growth has fallen to 3-4%. High levels of household debt and tighter bank lending standards discourage additional borrowing, despite further rate cuts.
NAB’s Chairman Phil Chronican made an interesting point in November 2019, noting that the RBA’s rate cuts were not achieving their goal of stimulating the Australian economy. He saw that when interest rates were cut, NAB’s borrowers were not reducing their monthly payments to spend on consumer goods, but were maintaining their monthly repayment to pay down their loan faster. Conversely, savers such as retirees living off term deposits – who are likely to spend all of their interest income – now face reduced cash flows. Thus, the fall in interest rates over the past decade appears to have resulted in a wealth transfer between savers who would otherwise be spending their interest income, to reduce the debts outstanding for borrowers. This transfer has affected a minimal positive impact on the economy.
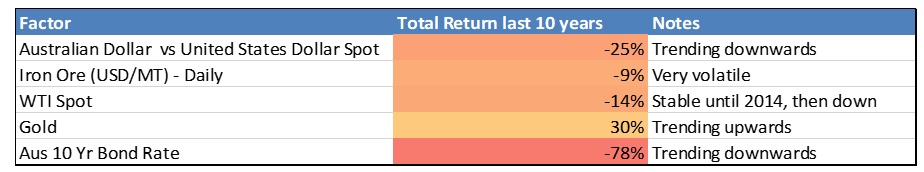
The falling oil price over the past decade has provided a consistent headwind for Woodside (+11%), Origin Energy (-12%) and Santos (-13%). However, decisions by Santos and Origin to spend tens of billions on competing LNG export plants at Gladstone in Queensland when the oil price was over US$100/bl (now US$60) has weighed on their share prices. The development of US shale gas in the early part of the decade changed the USA – one of the largest oil importers – to a nation that is now exporting energy globally. Arguably this is one of the major changes over the past decade, as it has damaged OPEC’s capacity to manipulate the global oil price and has revitalised US manufacturing, now powered by cheap US energy.
The Leaders of Today aren’t always the Leaders of the Future
The below table looks at how the ASX Top 50 stocks in December 2009 have performed over the past decade. Particularly striking is the distribution of the table, with only 17 of the Top 50 stocks outperforming the ASX 200, and the bulk of the Top 50 underperforming. This is because the performance of the index has been driven by companies that were either quite small in 2010 such as Magellan (+884%) or were still a twinkle in their founder’s eyes, such as Afterpay.
Ten per cent of the ASX Top 50 from December 2009, did not get a chance to shine over the full ten years as they were taken over by mostly foreign buyers. Generally, this was good news for Australian shareholders as Japan Post and SAB Miller clearly overpaid for their acquisitions of Toll and Fosters respectively, with both companies subsequently writing down the value of the transport and beer assets by billions. Though overpaying for ASX listed companies is not solely the province of foreigners, AMP’s $4.15 billion bid for AXA Asia Pacific in 2011 has proven to be a poor move.
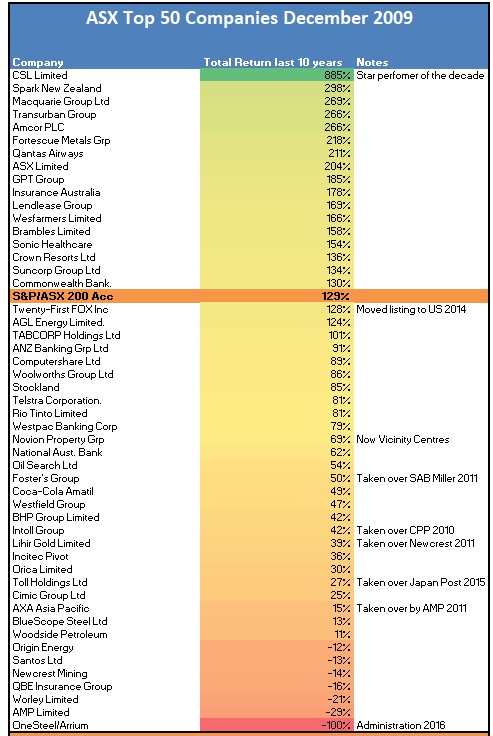
Top Performers on the ASX
The key themes among the leaders are companies that have grown earnings (CSL, Fortescue, Sonic Healthcare), benefited from falling interest rates (Transurban, GPT), and have enjoyed a tailwind from a falling Australian dollar (Amcor, Macquarie). The fall in the oil price has dramatically improved Qantas’ business model, transforming the company from one needing to raise capital to stay afloat to one that consistently conducts share buy-backs.
Bringing up the rear
Steelmaker Onesteel/Arrium is the worst-performing stock in the Top 50 over the past decade with the company going into administration in 2016 causing equity investors to lose their entire investment. The steel company’s long steel manufacturing operations and significant investment in some small high-cost iron ore mines in South Australia resulted in climbing debts and mounting losses.
However, several household names have also had a decade to forget. AMP (-29%) suffered due to a poor acquisition in AXA, along with rough treatment in the 2018 Royal Commission into Financial Services that exposed flaws in the 170-year-old company’s business model and has raised questions about its long-term viability. While QBE Insurance (-16%) has been a better performer over the past few years, for most of the 2010s management has been dealing with the hangover of an acquisition spree that saw QBE grow via acquisition into one of the Top 10 global insurers. Unfamiliar areas of business such as Argentinian workers compensation and Ecuadorian crop insurance resulted in large profit downgrades before these business units were sold.
Among the top 4 major banks, Commonwealth Bank (+130%) is the pick of the litter, though this result matches the ASX 200. Commonwealth Bank’s outperformance is likely due to its higher return on equity and lower loan losses compared with the other banks, as well as avoiding offshore adventures that have caused pain for NAB and ANZ’s shareholders. Against a background of falling credit growth, rising compliance costs and newly aggressive regulators levying heavy fines, ANZ (+91%) NAB (+62%) and Westpac (+79%) have all returned less than the ASX 200 over the past decade.
Our take
Overall the past decade has been better for equity investors than most fund managers would have predicted in December 2009, when large companies were still going under as a result of the GFC. The 130% return over the 2010s equates to a compound growth rate of 8.7% per annum, around the average for Australian equities since 1900. One of the biggest issues that all investors face is the relentless noise and news flow that often obscures the long-term trends for company earnings. What is clear from reflecting on the past decade is that companies that have successfully grown their share price over the long term require both astute management teams, but also some help from underlying economic trends outside of the company’s control. While top-performing companies such as CSL, Macquarie Bank and Amcor have all made successful acquisitions and grown their existing operations, they have also all enjoyed support from the tailwinds of decade long decline in the Australian dollar and falling interest rates.
This article also appears in Firstlinks Headwinds and tailwinds, a decade in review

